April 26, 2024
Most bees don’t die after stinging - and other surprising bee facts
99.96% of bee species do not die after stinging. So why does everyone think they do?
Most of us have been stung by a bee and we know it’s not much fun. But maybe we also felt a tinge of regret, or vindication, knowing the offending bee will die. Right? Well, for 99.96% of bee species, that’s not actually the case.
Only eight out of almost 21,000 bee species in the world die when they sting. Another subset can’t sting at all, and the majority of bees can sting as often as they want. But there’s even more to it than that.
To understand the intricacies of bees and their stinging potential, we’re going to need to talk about the shape of stingers, bee genitals, and attitude.
Our beloved, and deadly, honey bees
What you most likely remember getting stung by is the European honey bee (Apis mellifera). Native to Europe and Africa, these bees are today found almost everywhere in the world.
They are one of eight honey bee species worldwide, with Apis bees representing just 0.04% of total bee species. And yes, these bees die after they sting you.
But why?
We could say they die for queen and colony, but the actual reason these bees die after stinging is because of their barbed stingers. These brutal barbs will, most of the time, prevent the bee from pulling the stinger out.
Instead, the bee leaves her appendage embedded in your skin and flies off without it. After the bee is gone, to later die from her wound, the stinger remains lodged there pumping more venom.
Beyond that, bees and wasps (probably mostly European honey bees) are Australia’s deadliest venomous animals. In 2017–18, 12 out of 19 deaths due to venomous animals were because of these little insects. (Only a small proportion of people are deathly allergic.)
Talk about good PR.
So what is a stinger?
A stinger, at least in most bees, wasps and ants, is actually a tube for laying eggs (ovipositor) that has also been adapted for violent defence. This group of stinging insects, the aculeate wasps (yes, bees and ants are technically a kind of wasp), have been stabbing away in self-defence for 190 million years.
You could say it’s their defining feature.
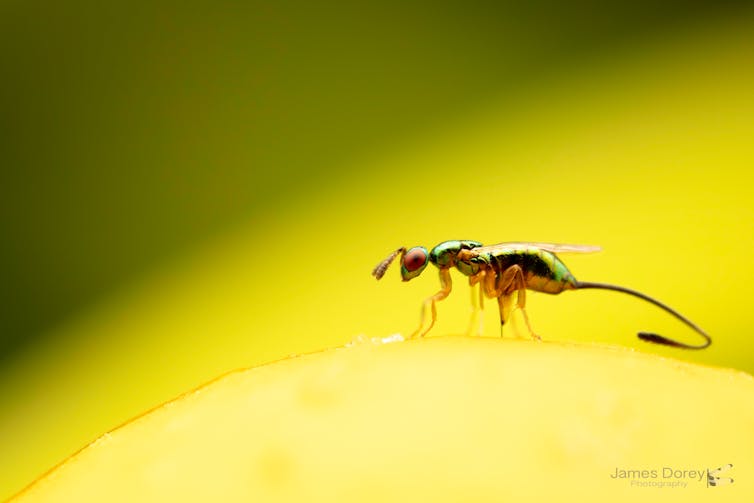

A Sycoscapter parasitoid wasp laying eggs into a fig through her ovipositor (bottom middle). James Dorey Photography
With so much evolution literally under their belts they’ve also developed a diversity of stinging strategies. But let’s just get back to the bees.
The sting of the European honey bee is about as painful as a bee sting gets, scoring a 2 out of 4 on the Schmidt insect sting pain index.
But most other bees don’t pack the same punch — though I have heard some painful reviews from less-than-careful colleagues. On the flipside, most bee species can sting you as many times as they like because their stingers lack the barbs found in honey bees. Although, if they keep at it, they might eventually run out of venom.
Even more surprising is that hundreds of bee species have lost their ability to sting entirely.
Can you tell who’s packing?
Globally, there are 537 species (about 2.6% of all bee species) of “stingless bees” in the tribe Meliponini. We have only 11 of these species (in the genera Austroplebeia and Tetragonula) in Australia. These peaceful little bees can also be kept in hives and make honey.
Stingless bees can still defend their nests, when offended, by biting. But you might think of them more as a nuisance than a deadly stinging swarm.
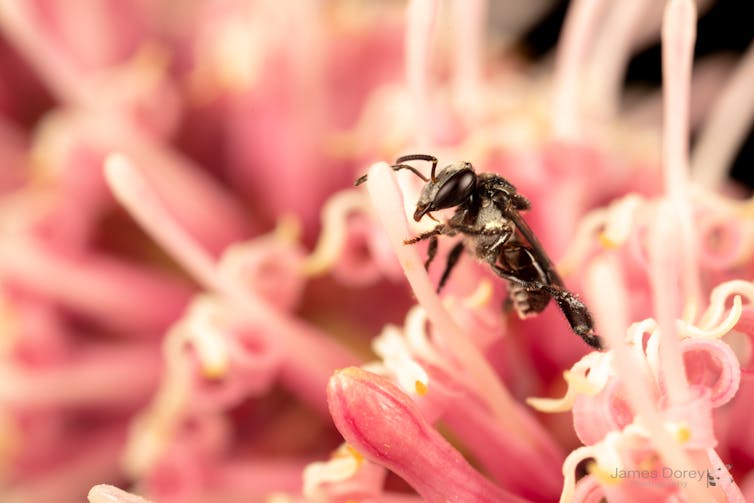

An Australian stingless bee, Tetragonula carbonaria, foraging on a Macadamia flower. James Dorey Photography
Australia also has the only bee family (there are a total of seven families globally) that’s found on a single continent. This is the Stenotritidae family, which comprises 21 species. These gentle and gorgeous giants (14–19mm in length, up to twice as long as European honey bees) also get around without a functional stinger.
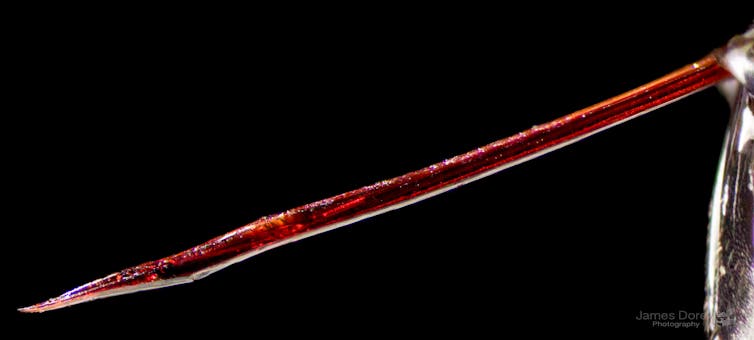
The long ovipositor of this parasitoid, and non-stinging, wasp is essentially a hypodermic needle for injecting an egg. James Dorey Photography
The astute reader might have realised something by this point in the article. If stingers are modified egg-laying tubes … what about the boys? Male bees, of all bee species, lack stingers and have, ahem, other anatomy instead. However, some male bees will still make a show of “stinging” if you try to grab them.
Some male wasps can even do a bit of damage, though they have no venom to produce a sting.
Why is it always the honey bees?
So, if the majority of bees can sting, why is it always the European honey bee having a go? There are a couple of likely answers to that question.
First, the European honey bee is very abundant across much of the world. Their colonies typically have around 50,000 individuals and they can fly 10km to forage.
In comparison, most wild bees only forage very short distances (less than 200m) and must stay close to their nest. So those hardworking European honey bees are really putting in the miles.
Second, European honey bees are social. They will literally die to protect their mother, sisters and brothers. In contrast, the vast majority of bees (and wasps) are actually solitary (single mums doing it for themselves) and lack the altruistic aggression of their social relatives.
A complicated relationship
We have an interesting relationship with our European honey bees. They can be deadly, are non-native (across much of the world), and will aggressively defend their nests. But they are crucial for crop pollination and, well, their honey is to die for.
But it’s worth remembering these are the tiny minority in terms of species. We have thousands of native bee species (more than 1,600 found so far in Australia) that are more likely to simply buzz off than go in for a sting.![]()
James B. Dorey, Lecturer in Biological Sciences, University of Wollongong; Amy-Marie Gilpin, Lecturer in Invertebrate Ecology, Western Sydney University, and Rosalyn Gloag, School of Life and Environmental Sciences Research Fellow, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
UOW academics exercise academic freedom by providing expert commentary, opinion and analysis on a range of ongoing social issues and current affairs. This expert commentary reflects the views of those individual academics and does not necessarily reflect the views or policy positions of the University of Wollongong.
:format(jpg)/prod01/channel_3/assets/media-centre/Bee-stings-James-Dorey-499X281.jpg)